Grief can lead to anxiety disorders, making recovery difficult for some. Key insights:
- Grief and Anxiety Link: Loss disrupts emotional balance, sometimes causing prolonged anxiety or depression.
- Warning Signs: Sleep issues, constant worry, and social withdrawal may signal anxiety disorders like GAD or PTSD.
- Coping Strategies: Therapy (like CBT), mindfulness, physical activity, and social support help manage symptoms.
- Professional Help: Early intervention is crucial, especially if symptoms persist for over six months.
Takeaway: Address grief-related anxiety early with tools like therapy, tracking apps, and support networks to regain emotional stability.
How Grief Affects Your Brain And What To Do About It
Mechanisms of Grief-Induced Anxiety
Grief and anxiety are closely connected through psychological processes that can significantly impact mental health. These mechanisms shed light on how anxiety disorders may emerge during periods of grief.
Loss of Control and Heightened Vulnerability
Grief often disrupts a person’s sense of security and control, leaving them feeling exposed and uncertain. Research highlights increased brain activity in areas that regulate emotions. This can lead to heightened alertness, emotional overwhelm, avoidance behaviors, and a tendency to seek out safety measures, even when unnecessary.
Stress and the Role of Rumination
Dwelling on negative thoughts, or rumination, can trap individuals in a cycle of anxiety. Studies show that people who ruminate after a loss are more likely to develop anxiety disorders. These thought patterns often revolve around the loss itself, self-doubt, fears about the future, or existential questions, making it harder to break free from the cycle.
The Impact of Social Isolation
Social isolation can make it harder to recover from grief and anxiety. Being cut off from others limits emotional processing and reduces access to crucial support systems. Without social connections, individuals may struggle with:
- Expressing emotions
- Receiving practical help
- Challenging anxious thoughts
- Moving forward and adjusting to their loss
Recent research reveals that 23% of adult psychiatric outpatients with mood and anxiety disorders also experience complicated grief. Recognizing these patterns is key to addressing anxiety disorders that arise during grief.
Identifying Anxiety Disorders in Grief
Understanding how to spot anxiety symptoms during grief can help differentiate between typical grief reactions and clinical anxiety disorders.
Signs of Grief-Related Anxiety
Here are some key indicators that anxiety linked to grief might be progressing into a disorder:
| Warning Sign | Description |
|---|---|
| Physical Symptoms | Tightness in the chest, high blood pressure, sweating, rapid heartbeat, muscle tension |
| Persistent Worry | Constant fear of future losses that disrupts daily life |
| Concentration Issues | Trouble focusing on tasks or making decisions for an extended period |
| Social Withdrawal | Avoiding social interactions and isolating more than usual |
| Panic Symptoms | Repeated panic attacks with symptoms like shortness of breath and chest pain |
When these signs persist or worsen, they may indicate an anxiety disorder linked to grief.
Anxiety Disorders Linked to Grief
Prolonged grief lasting more than six months and interfering with daily functioning, often referred to as complicated grief, is closely tied to anxiety disorders that may need professional attention.
Some of the most common anxiety disorders associated with grief include:
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD): Involves ongoing worry about future losses or safety, often heightened by grief.
- Panic Disorder: Marked by frequent panic attacks and overwhelming fear, often triggered by grief-related memories or situations.
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): Can arise after a traumatic loss, leading to intrusive thoughts, flashbacks, and avoidance behaviors.
"People who experience intense grief symptoms that interfere with daily life and occur more than 6 months after a loss may have complicated grief, which is frequently associated with an anxiety disorder." – HealthCentral
Physical symptoms like dizziness, nausea, stomach cramps, and fatigue are also common. The main distinction between grief and anxiety disorders lies in how long the symptoms last, how severe they are, and their impact on a person’s life.
sbb-itb-b1dedcc
Coping Strategies for Grief and Anxiety
Dealing with grief-related anxiety often involves a mix of professional guidance and practical self-help techniques. Studies suggest that addressing emotions and improving confidence in handling challenges can lead to better outcomes.
Professional Support and Therapy
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is particularly effective for managing anxiety tied to grief. It helps individuals reshape negative thoughts and develop healthier ways to cope. Research highlights that 64% of grieving individuals may experience pathological grief.
Key components of therapy include:
| Treatment Component | Purpose | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Cognitive Restructuring | Shifts unhelpful thought patterns | Reduces anxiety |
| Exposure Therapy | Confronts grief-related triggers | Reduces avoidance |
| Skills Training | Builds coping techniques | Enhances emotional control |
While therapy offers structured support, self-help methods can make a big difference in managing grief day-to-day.
Building Healthy Coping Strategies
Studies show that structured approaches to grieving are linked to lower anxiety and depression levels. Some effective strategies include:
- Mindfulness Practice: Helps reduce overthinking and promotes awareness.
- Physical Activity: Boosts mood by releasing endorphins.
- Social Connection: Provides emotional support during tough times.
"Difficulties in emotion regulation and lower perceived self-efficacy were associated with greater severity of PGD." –
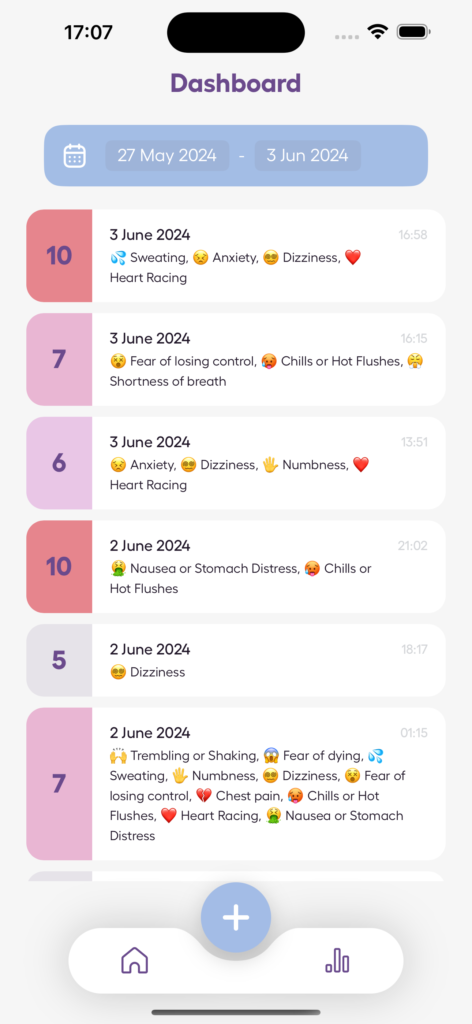
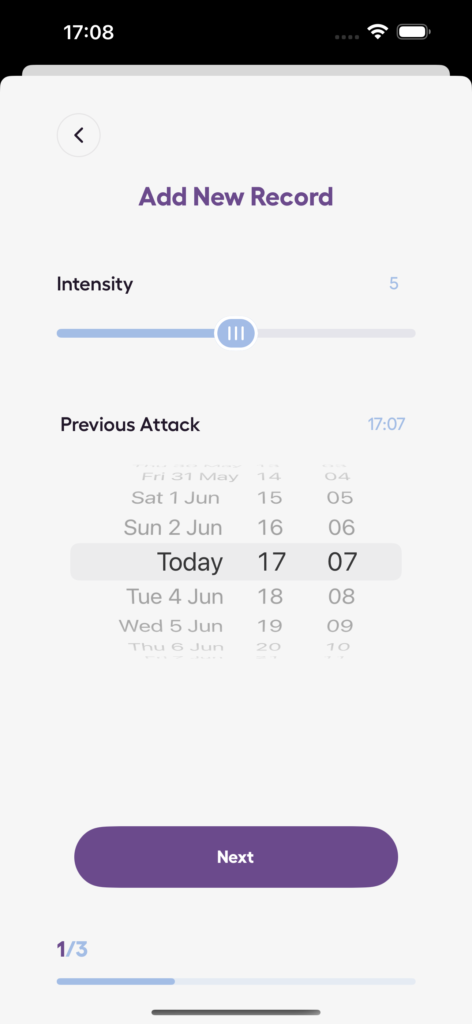
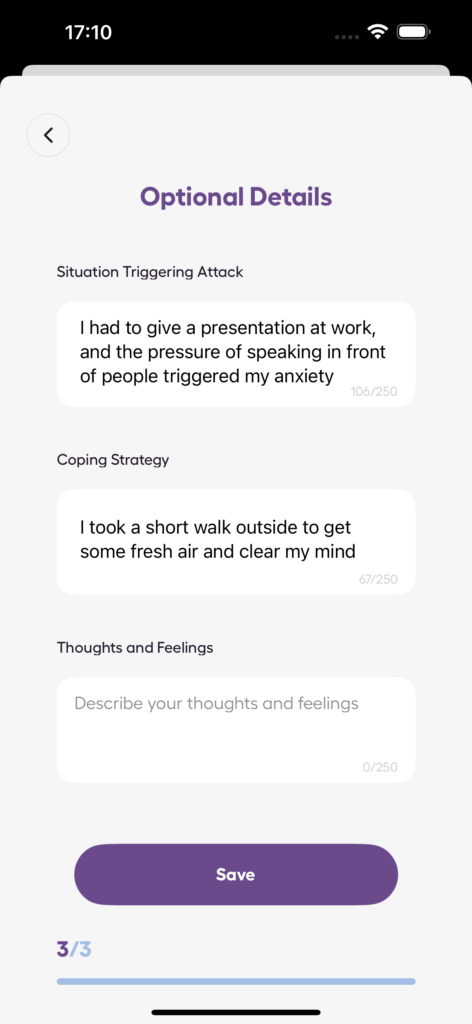
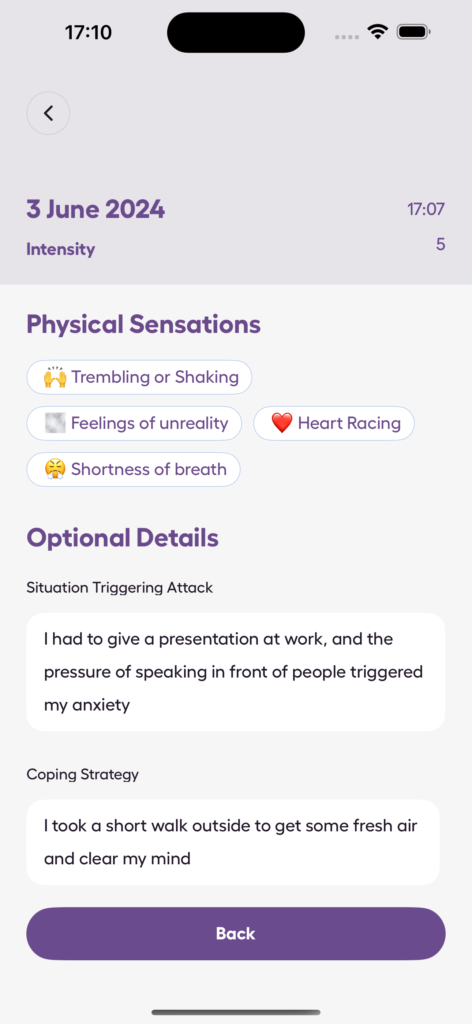
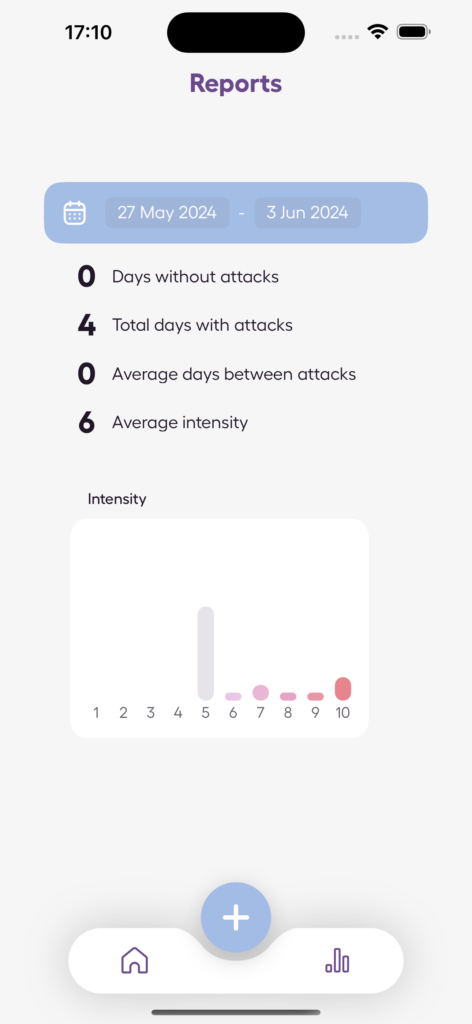
Using the Anxiety Journal App
For those looking to better understand their emotions and track progress, tools like the Anxiety Journal app can be incredibly helpful. This app allows users to monitor stress, track panic attacks, and assess anxiety levels. Its features are designed to support the grieving process through:
- Tracking anxiety patterns over time.
- Monitoring emotional states regularly.
- Tools for measuring progress.
- Secure space for personal reflections.
Long-Term Recovery and Resilience
Recovering from grief-related anxiety involves a deliberate focus on healing and personal development. Studies reveal that people who learn effective ways to manage their emotions tend to handle grief and anxiety more effectively in the long run.
Acceptance and Finding Meaning
Reaching a place of acceptance means recognizing the loss while adopting new perspectives. Research shows that struggles with regulating emotions can intensify grief-related anxiety.
"Difficulties in emotion regulation and lower perceived self-efficacy were associated with greater severity of PGD." –
Activities like creating memorials, participating in charitable initiatives, or joining support groups can provide a sense of closure and connection, honoring the loss in a meaningful way.
Growth After Trauma
Adversity can sometimes lead to emotional growth, a process referred to as post-traumatic growth. For instance, Adult Separation Anxiety Disorder (ASAD) is reported to affect 43% of adult psychiatric outpatients with mood and anxiety disorders. This growth often appears in unexpected ways, helping individuals develop better coping skills and emotional strength.
As acceptance becomes part of the healing process, many people discover opportunities to strengthen their emotional resilience. This growth not only helps reduce the impact of grief-related anxiety but also equips individuals to face future challenges. However, sustaining this progress requires ongoing attention to anxiety management.
Ongoing Anxiety Management
Research into how the brain processes prolonged grief highlights the importance of tailored interventions. Key approaches include:
- Regularly tracking emotions with structured tools.
- Staying connected with mental health professionals.
- Using proven methods to address anxiety triggers.
Tools like the Anxiety Journal app can be particularly helpful, offering a way to monitor progress and support emotional well-being throughout recovery.
Conclusion: Steps Toward Healing
Main Points
Grief-related anxiety poses a serious mental health challenge that demands careful attention and specific strategies. The connection between grief and anxiety is shaped by distinct neural pathways, setting it apart from other mental health conditions.
Navigating grief-induced anxiety requires identifying emotional patterns and adopting effective coping techniques. Difficulties with managing emotions and a sense of self-efficacy are closely linked to intense grief symptoms. This understanding has paved the way for interventions aimed at strengthening emotional resilience and developing practical coping methods.
Encouraging Support Seeking
Studies show that around 56% of individuals with complicated grief also experience adult separation anxiety disorder. This highlights the importance of seeking professional help early in the grieving process.
Here are some steps that can help individuals regain emotional stability and control:
- Reach out for professional counseling or join grief support groups.
- Use tools like the Anxiety Journal app to monitor anxiety levels and identify triggers.
- Stay connected with friends, family, and other support networks.
The Anxiety Journal app offers features like tracking anxiety episodes and monitoring stress, providing insights that are helpful for both individuals and their healthcare providers.
Grief can often lead to withdrawal, making it even more crucial to seek support and maintain connections. With the right mix of professional help, self-monitoring tools, and emotional support, recovery is achievable.