Does social media make your teen anxious? Social media anxiety is common among teens and can stem from comparison, FOMO (fear of missing out), and online pressures. Here’s how you can help:
- Recognize warning signs: Mood swings, withdrawal, poor sleep, or defensiveness about social media use.
- Set boundaries: Limit screen time, create device-free zones, and curate positive content.
- Encourage offline activities: Sports, art, or volunteering can boost confidence and reduce digital stress.
- Use tracking tools: Apps like Anxiety Journal can help identify triggers and manage anxiety.
Start with small, actionable steps to help your teen build a healthier relationship with social media.
Parents: 4 Tips to Help Teens with Social Media & Mental …
Social Media Anxiety Basics
Social media anxiety stems from the digital pressures that amplify stress, especially among teens.
How Social Media Affects Teen Mental Health
The teen years are crucial for building identity and navigating social connections. These factors make adolescents particularly vulnerable to online stress, including:
- Constant comparisons: Seeing others’ carefully curated posts can chip away at self-esteem.
- Validation pressure: Chasing likes, comments, and shares can become a major source of stress.
Common Triggers of Social Media Anxiety
Certain aspects of social media often fuel anxiety for teens:
- Pressure to maintain a perfect image: Teens, who are still learning to manage emotions, may feel overwhelmed by the need to create an ideal online persona.
- Fear of missing out (FOMO): Seeing posts about events they weren’t part of can heighten feelings of exclusion.
- Cyberbullying: Hurtful comments or online criticism can lead to significant emotional pain.
- Peer comparison: Constantly measuring themselves against others online can deepen insecurities.
Up next, the Warning Signs section will help you identify how these stressors might show up in your teen’s behavior.
Warning Signs in Teens
Key Behavior Changes to Watch For
Spotting social media anxiety in teens often requires paying close attention to changes in their behavior. Here are some shifts that could signal your teen is having a tough time:
Emotional Changes
- Frequent mood swings after spending time online
- Becoming defensive when asked about their social media use
- Feeling anxious when away from their phone or during screen breaks
Social and Academic Patterns
- Pulling back from face-to-face activities or friends
- Checking social media during family meals
- Struggling with grades or finding it hard to focus
Physical Changes
- Difficulty sleeping, staying up late, or feeling tired throughout the day
If these patterns continue or get worse, it might be time to explore professional help.
Signs to Contact a Professional
Some level of anxiety tied to social media is common, but certain behaviors should raise concern and may need immediate attention:
Urgent Warning Signs
- An inability to step away from social media, even briefly
- Persistent feelings of hopelessness or self-critical thoughts
- Any mention of or actions related to self-harm
Using tools like the Anxiety Journal Panic Attack & Anxiety Tracker app can help track these behaviors and uncover patterns that mental health professionals can address. Early action is key – don’t wait for multiple red flags. Even one serious sign is enough to seek support, as addressing social media anxiety early can make a big difference for teens.
sbb-itb-b1dedcc
Parent Action Steps
Setting Social Media Boundaries
Establish clear daily time limits for social media use and designate device-free zones like during meals or homework time. Work together to create rules that encourage self-discipline while respecting family routines. Also, help your child curate their feeds to minimize exposure to content that may trigger stress or anxiety.
Encouraging Healthier Online Habits
Regularly review the content they follow. Suggest unfollowing accounts that contribute to anxiety and replacing them with profiles focused on education, mental health, or personal interests. Encourage them to reflect on their social media interactions by asking these three questions:
- Is this image edited or filtered?
- What’s the purpose of this post?
- How does this content make me feel?
These simple steps can help reduce impulsive reactions and make scrolling a more positive experience. Pair these online adjustments with activities that build confidence offline.
Boosting Confidence Through Real-Life Activities
Engage in offline activities to strengthen self-esteem. Some ideas include:
- Sports: Soccer, running, yoga, or family hikes
- Creative Outlets: Art classes, music lessons, or journaling
- Community Engagement: Volunteering, youth leadership programs, or joining school clubs
Consider using tools like the Anxiety Journal app to track moods during online and offline activities. This can help identify patterns and make it easier to adjust habits for a healthier balance.
Anxiety Tracking Methods
Using tools like Anxiety Journal alongside social media guidelines and offline strategies can help identify anxiety triggers and monitor progress over time.
How Anxiety Apps Help
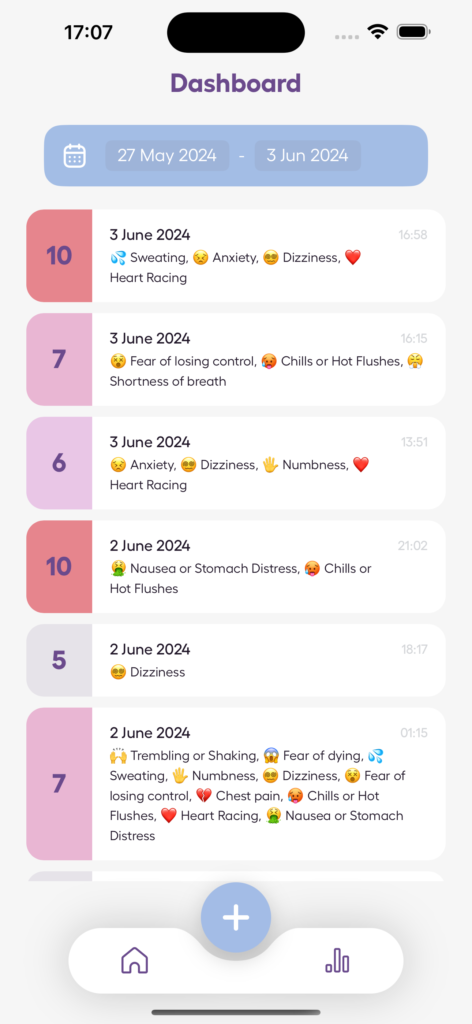
Anxiety-tracking apps can assist teens in recognizing how social media affects their anxiety and tracking their emotional well-being. Here’s what Anxiety Journal offers:
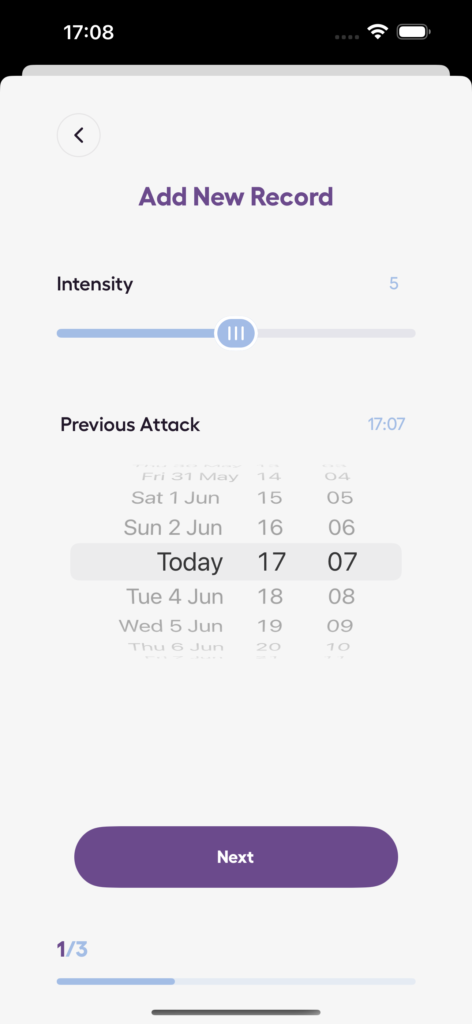
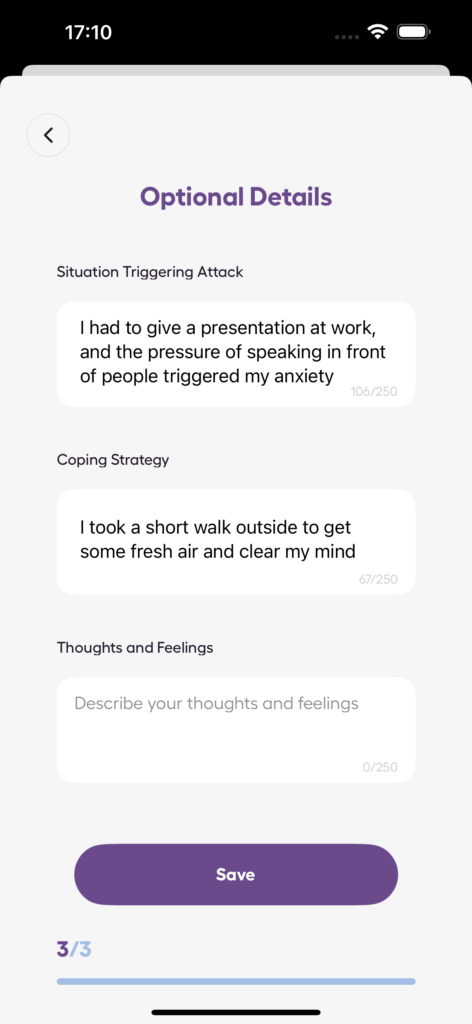
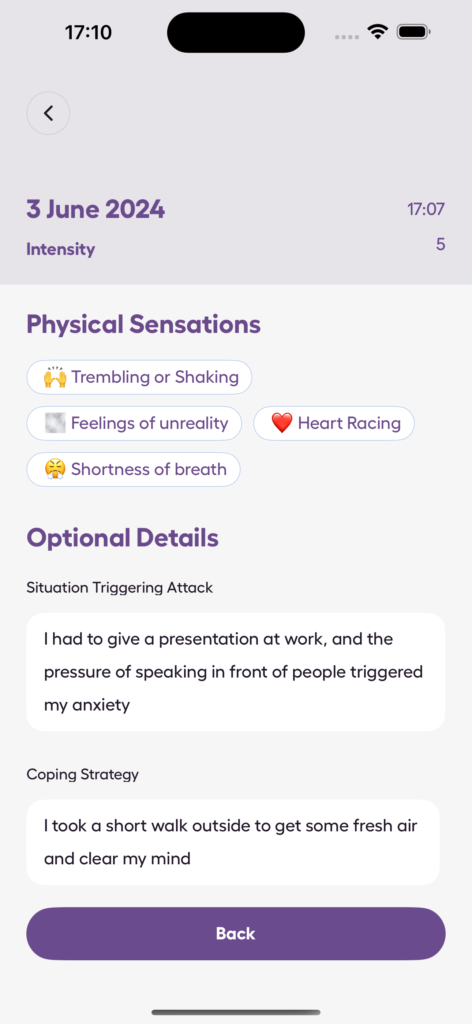
- Log anxiety episodes: Record symptoms, triggers, thoughts, and coping methods.
- AI insights: Identify connections between social media use and anxiety spikes.
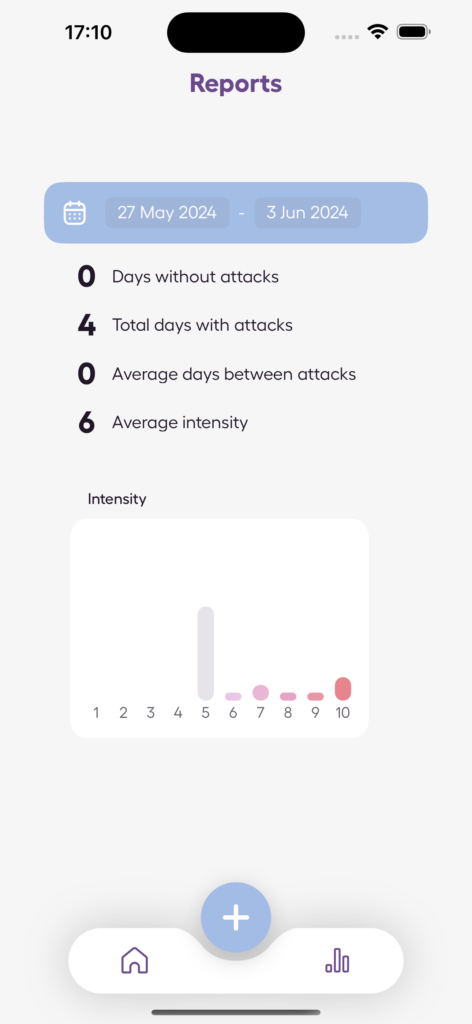
- Visual progress reports: Spot trends and track improvements through easy-to-read charts.
- Built-in assessments: Regularly complete tools like the GAD-7 to measure anxiety levels.
- Guided breathing exercises: Access calming techniques for quick relief.
Daily Anxiety Tracking Tips
Help teens establish a consistent tracking habit with these suggestions:
- Record entries when anxiety arises – before, during, or after social media use.
- Tag entries by platform or type of content to pinpoint specific stressors.
- Review weekly summaries to acknowledge progress and spot recurring patterns.
- Complete monthly GAD-7 assessments to monitor long-term changes.
- Use guided breathing exercises whenever feeling overwhelmed.
Go over the data together to adjust habits and encourage open conversations about mental health.
Conclusion
Helping teens handle social media anxiety involves a mix of parental support, clear rules, consistent monitoring, and honest conversations. These steps are key to building confidence and resilience in the digital world.
Apps like Anxiety Journal can assist teens by allowing them to track their feelings, identify trends using AI, and practice calming techniques like guided breathing. Combining these tools with regular monitoring, parental involvement, limited screen time, and encouraging offline activities can create a strong foundation for supporting teens’ mental health.